OneDQuantum.OneDSchrodinger module¶
This module contains OneDSchrodinger functions. It is a Python interface of 1DSchrodinger.c
-
class
ErwinJr2.OneDQuantum.OneDSchrodinger.Band(bandtype, *args, **kwargs)¶ Python interface for a Band
-
ErwinJr2.OneDQuantum.OneDSchrodinger.cBandFillPsi(step, EigenEs, V, band, xmin=0, xmax=None, Elower=None, Eupper=None, field=None)¶ Find wave functions using band mass. field, Elower and Eupper is used only for bound the energy range of the wave functions: outside the bound the wavefunction is promised to be zero.
- Return type
-
ErwinJr2.OneDQuantum.OneDSchrodinger.cBandSolve1D(step, Es, V, band, xmin=0, xmax=None)¶ Find eigen energies using band mass.
- Return type
-
ErwinJr2.OneDQuantum.OneDSchrodinger.cSimpleFillPsi(step, EigenEs, V, m, xmin=0, xmax=None)¶ Find wave functions. Assume mass as given.
- Return type
-
ErwinJr2.OneDQuantum.OneDSchrodinger.cSimpleSolve1D(step, Es, V, m, xmin=0, xmax=None)¶ Find eigen energies. Assume mass as given.
- Return type
Example¶
Here is an example for how to use OneDSchrodinger.py for 1D triangle well.
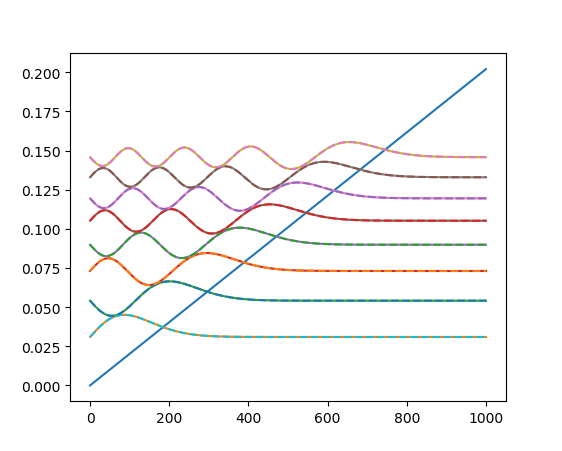
Output of SimpleSchrodinger.py¶
#!/usr/bin/env python3
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
from context import *
from OneDQuantum import *
from pylab import *
from scipy.constants import hbar, e, m_e, pi
ANG=1E-10
def square_well(x0=0, x1=100, x2=300, x3=400, Vmax=0.287):
"""
Solve quantum for V = Vmax (x0<x<x1 or x2<x<x3), 0 (x1<x<x2)
"""
x = np.linspace(x0, x3, 1000)
step = x[1]-x[0]
V = np.zeros(x.shape)
V[(x < x1) | (x >= x2)] = Vmax
mass = 0.067
Es = np.linspace(0, 0.2, 100)
EigenEs = cSimpleSolve1D(step, Es, V, mass)
psis = cSimpleFillPsi(step, EigenEs, V, mass)
print("Eigen Energy: ", EigenEs)
plot(x, V)
for n in range(0, EigenEs.size):
plot(x, EigenEs[n] + psis[n, :]/np.max(psis[n, :])*0.01)
return x, V, EigenEs, psis
def triangle_well(F, xmax=1E3):
x = np.linspace(0, xmax, 5000)
step = x[1]-x[0]
V = F * (xmax - x)
mass = 0.067
Es = np.linspace(0, 0.15, 100)
EigenEs = cSimpleSolve1D(step, Es, V, mass)
psis = cSimpleFillPsi(step, EigenEs, V, mass)
# an = np.arange(0, 8) + 0.75
# EigenEs_th = (hbar**2/(2*m_e*mass*e*ANG**2)*(3*pi*F*an/2)**2)**(1/3)
# Above is approximate Airy zeros result
from scipy.special import airy, ai_zeros
an = ai_zeros(8)[0]
EigenEs_th = -(hbar**2*F**2/(2*m_e*mass*e*ANG**2))**(1/3)*an
psis_th = np.array([
airy((2*mass*m_e*e*ANG**2*F/hbar**2)**(1/3) * (x-E/F))[0]
for E in EigenEs_th])
psis_th /= (np.linalg.norm(psis_th, axis=1) * sqrt(step))[:, None]
V = np.ascontiguousarray(V[::-1])
psis = np.ascontiguousarray(psis[:, ::-1])
print("Eigen Energy: ", EigenEs)
print("Thoery: ", EigenEs_th)
print("Diff: ", EigenEs - EigenEs_th)
plot(x, V)
scale = 0.15
for n in range(0, EigenEs.size):
plot(x, EigenEs[n] + psis[n, :]*scale)
for n in range(0, EigenEs_th.size):
plot(x, EigenEs_th[n] + psis_th[n, :]*scale, '--')
return x, V, EigenEs, psis, EigenEs_th, psis_th
if __name__ == "__main__":
x, V, EigenEs, psis = square_well()
show()
x, V, EigenEs, psis, EigenEs_th, psis_th = triangle_well(2.02e-4)
show()